Next.js version
"next": "13.2.4”
Setting up the library
npm install next-auth
npm install @next-auth/mongodb-adapter
With the Next-auth library, all methods are JWT by default.
It does not store user session data in the DB, but only sends JWT to the user.
When the user visits a page that requires login, only the JWT submitted by the user is checked and admitted.
If you want to create a session-based membership feature, you can use the DB adapter feature.
If you turn on the DB adapter feature
- It automatically registers the user at the first login and keeps the user’s membership information in the DB.
- When you log in, it automatically keeps session information in the DB about when the user logged in.
- If the server needs the currently logged-in user information, it retrieves the session information from the DB, not the JWT.
- When logging out, user session information is deleted from the DB.
So if you need to store the registered user information in the DB or if you want to strictly manage the user login status
If you want to strictly manage user login status, you can use the DB adapter function.
Setting up the MongoDB adapter
If you want to store user sessions in a DB other than MongoDB, you can find and use another DB adapter.
import { connectDB } from "@/util/database";
import { MongoDBAdapter } from "@next-auth/mongodb-adapter";
import NextAuth from "next-auth";
import GithubProvider from "next-auth/providers/github";
export const authOptions = {
providers: [
GithubProvider({
clientId: process.env.CLIENT_ID,
clientSecret: process.env.CLIENT_PW,
}),
],
secret: process.env.JWT_SECRET,
adapter: MongoDBAdapter(connectDB), // added
};
export default NextAuth(authOptions);
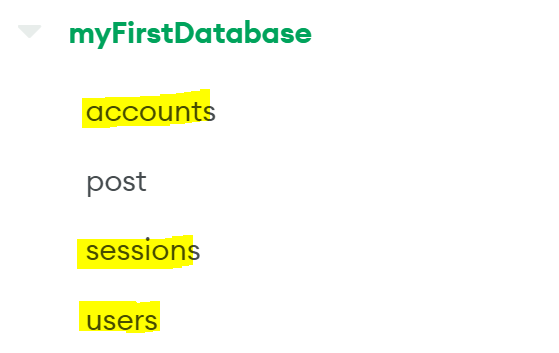
▲ When you log in, you’ll see that three collections have been created in MongoDB, unlike last time.
The ``sessions` contains the currently logged in user information. It also contains the login expiration date
users is where users are stored. Users are separated by email.
The accounts is where user accounts are stored.
Because a user can have multiple accounts, there may be duplicate emails for each account.
Q. What is the difference between users vs accounts?
Let’s say a user signs up for your site with Github and Google.
But this person’s
Github account is test@naver.com
And their Google account is test@naver.com.
In this case, the users collection would only have one document with the
test@naver.com and only one document with the email test@naver.com is created in the
accounts collection contains
- test@naver.com + document with Github in it
- test@naver.com + a document with Google
This creates two documents.
In this way, you can create 1 user but 2 or more accounts.
(If they have the same email, we automatically assume they are the same user)
session to use the
We want to make it possible for the user to delete a previously created post.
let session = await getServerSession(req, res, authOptions)
Now we need to
Let’s add this feature on the server so that when a post is created, the user information is sent to the DB.
pages/api/write.js
import { connectDB } from "util/database";
import { getServerSession } from "next-auth";
import { authOptions } from "./auth/[...nextauth]";
const handler = async (req, res) => {
if (req.method == "POST") {
let session = await getServerSession(req, res, authOptions);
if (session) {
req.body.author = session.user.email;
} else {
return res.status(400).json("Available after signing in.");
}
const { title, content, author } = req.body;
if (title == "" || content == "") {
return res.status(200).redirect(302, "/write");
}
const db = (await connectDB).db("forum");
const result = await db.collection("post").insertOne({
title,
content,
author,
});
console.log(
"The user has entered information ->" +
"title " +
title +
" " +
"content " +
content +
" " +
"author " +
author
);
return res.status(200).redirect(302, "/list");
} else {
return res.status(400).json("This is an incorrect approach.");
}
/**
* If the DB is down or the internet is disconnected or something like that, errors may occur in the DB.
If you want to check for such cases,
let's use try, catch. The try, catch syntax is try { } If the code inside the catch fails,
the code inside the catch { } will be executed instead.
*/
};
export default handler;
Add author field to distinguish users when creating posts
pages/api/post/delete.js
import { connectDB } from "util/database";
import { ObjectId } from "mongodb";
import { getServerSession } from "next-auth";
import { authOptions } from "../auth/[...nextauth]";
export default async function handler(req, res) {
if (req.method !== "POST") {
return res.status(400).json("Not the right approach");
} else {
let session = await getServerSession(req, res, authOptions);
if (session) {
console.log(session);
try {
const { uid } = req.query;
const db = (await connectDB).db("forum");
const dbmore = await db
.collection("post")
.findOne({ _id: new ObjectId(uid) });
if (session.user.role == "admin") {
const result = await db
.collection("post")
.deleteOne({ _id: new ObjectId(uid) });
return res.status(200).send(result);
} else if (dbmore.author !== session.user.email) {
res.status(400).json("Not the right approach");
} else {
const result = await db
.collection("post")
.deleteOne({ _id: new ObjectId(uid) });
return res.status(200).send(result);
}
} catch (error) {
return res.status(500);
}
} else {
return res
.status(400)
.json("You don't have permission to delete the post.");
}
}
}
If user.role is admin, we added the permission to delete the post even if the user is not the author of the post because they are an administrator.
This comparison statement can be used to determine if the user is the author of the post: dbmore.author !== session.user.email.
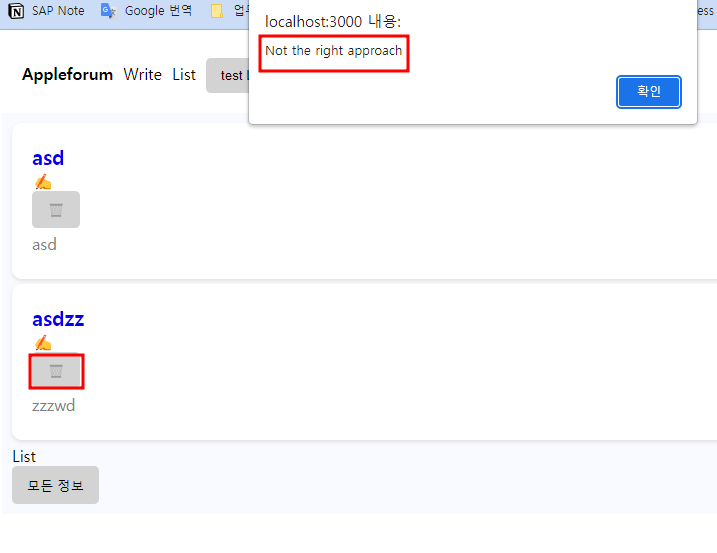
If you are not the amin or the author of the post, return the following result
